1. What is CDA?
In semiconductor manufacturing, CDA is commonly referred to as Compressed Dry Air or Clean Dry Air. Due to the presence of moisture in the atmosphere, it cannot be directly used in semiconductor processes. CDA, on the other hand, does not contain moisture or oil. In semiconductor fabs, CDA mainly supplies power gas source and purge for pneumatic equipment, as well as local scrubber combustion assistance. The pressure used in semiconductor fabs is relatively high compared to the general industry, commonly above 8.5 bar.
2. The role of CDA
The main uses of CDA in semiconductor manufacturing include the following aspects:
(1) Equipment blowing and cleaning
CDA is used to clean the surface and internal components of semiconductor manufacturing equipment, ensuring a dust-free and moisture free operating environment.
It can blow away tiny particles on the device, preventing them from contaminating wafers or other critical components.
(2) Pressure system control
CDA can serve as a pressure source to provide stable air pressure support for various equipment and tools, such as vacuum pumps, valves, etc.
In some cases, CDA can also be used as an inert gas to protect equipment from oxidation or other chemical reactions.
(3) Transport other gases
CDA is often used to transport other high-purity process gases (such as ammonia, hydrogen, etc.) by blowing pipelines to keep the gas transmission system clean and dry.
(4) Cooling and heat exchange
In some applications, CDA can be used for the cooling system of equipment to help regulate temperature.
(5) Emergency protection
When an emergency occurs, CDA can be used to blow or dilute harmful gases to ensure the safety of personnel and equipment.
3. Characteristics of CDA
In order to meet the high requirements of semiconductor manufacturing, CDA must possess the following characteristics:
(1) High cleanliness
CDA must be filtered to ensure that the particle diameter is less than 0.1 microns and contains almost no impurities.
The moisture content in the air must be extremely low, usually reaching a dew point of -40 ° C or lower.
(2) Dryness
Moisture can have a serious impact on the semiconductor manufacturing process, so CDA must be dry and typically requires removal of moisture.
(3) Stability
CDA should have good chemical stability and not react with equipment or materials.
(4) High voltage supply
CDA is usually supplied at higher pressures (such as 6-8 bar) to meet the needs of different equipment.
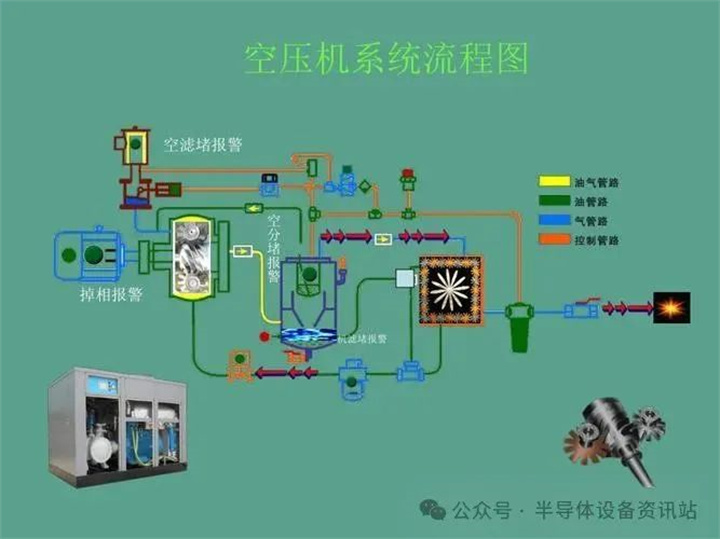
4. Preparation and delivery of CDA
The preparation and delivery of CDA require the following steps:
(1) Air compression
Use an air compressor to compress ordinary air to the required pressure.
(2) Filtration and drying
Compressed air needs to pass through multi-stage filters to remove dust, particles, and other impurities.
Next, reduce the moisture content in the air through a freeze dryer or adsorption dryer.
(3) Transportation and Distribution
The purified CDA is transported to various workshops and equipment through pipelines, usually using stainless steel pipes to ensure cleanliness.
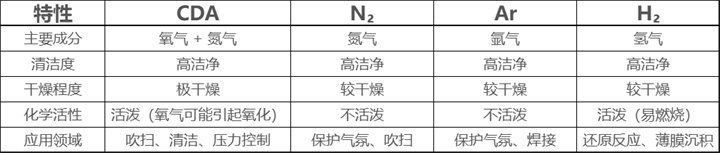
5. Difference between CDA and other gases